Backed by Science: Over 40 scientific studies show that the main ingredient in Iso-Alpha improves:
Real World Results
-

John Gingas
Wealth Manager
"They are my happy pills!" -

Micah Lowe
Founder of Simply 03 & Theriome
"My mood has improved and my short-term memory recall is noticeably better" -

Dan Vinton
Advertising Executive
"I’ve seen a noticeable difference in mood and clarity."

90 day "Brain Boost" Guarantee
When you take Iso-Alpha you will see that your brain starts to function a bit better each day. This is not an instant recovery but over time (60 days is recommended) you will likely see memory, focus and function improve.
The Key: Hacking the Gut/Brain Connection
-
STEP 1: Gut
The extremely bitter-tasting iso-alpha acids in Iso-Alpha act on the Bitter Taste Receptors in the gut.
-

STEP 2: Vagus Nerve
The gut hormone CCK stimulates the vagus nerve - the connection between the gut and the brain.
-

STEP 3: Brain
The vagus nerve signals the brain to release more acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and dopamine.
Special Pricing For First-Time Customers!
Try Iso-Alpha

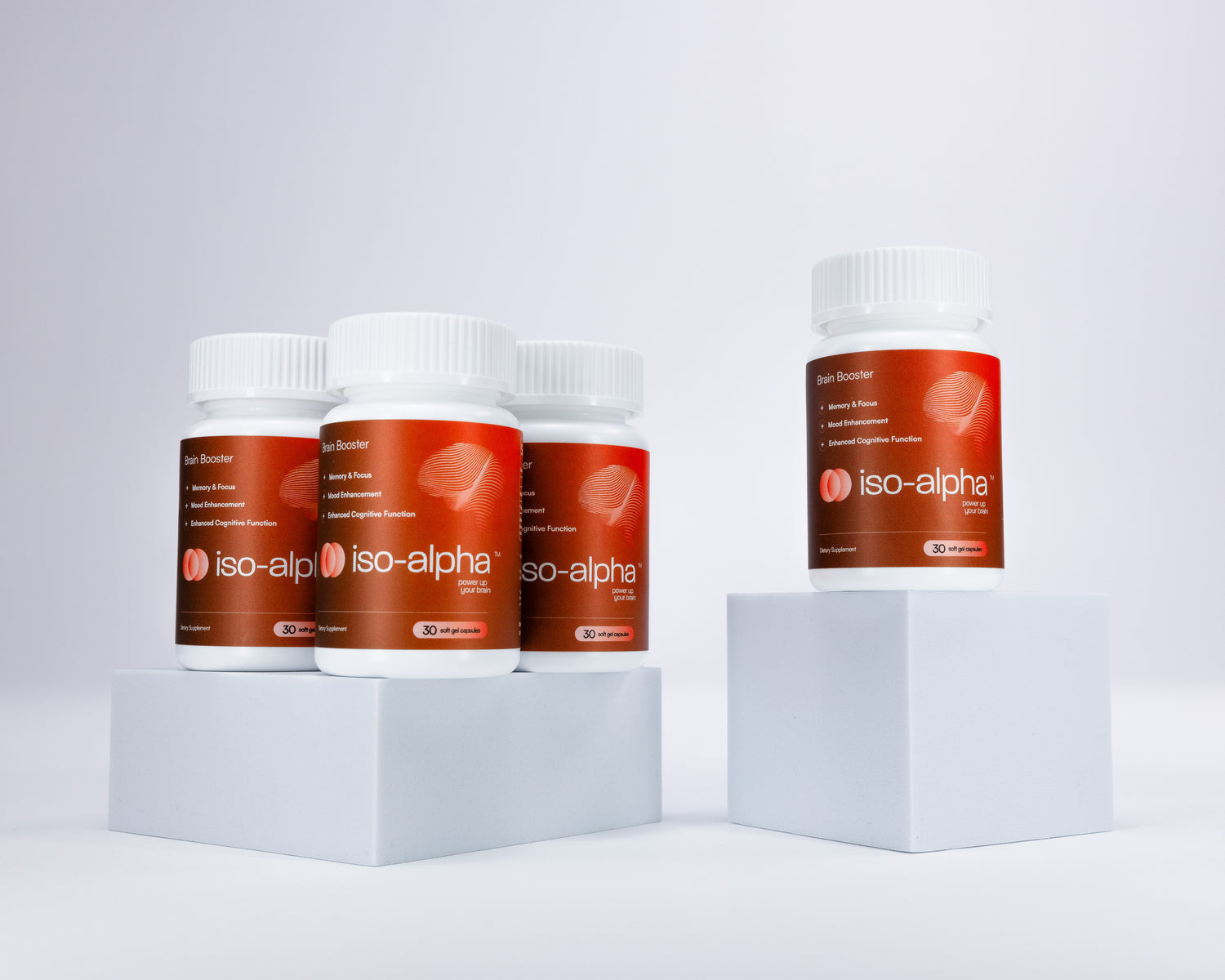
What's Inside
Inside each Iso-Alpha bottle you will find a 30-day supply of brain fuel.
Our bioavailable formula swiftly targets receptors upon ingestion, triggering a hormone release that stimulates the Vagus Nerve – a crucial pathway in the body.
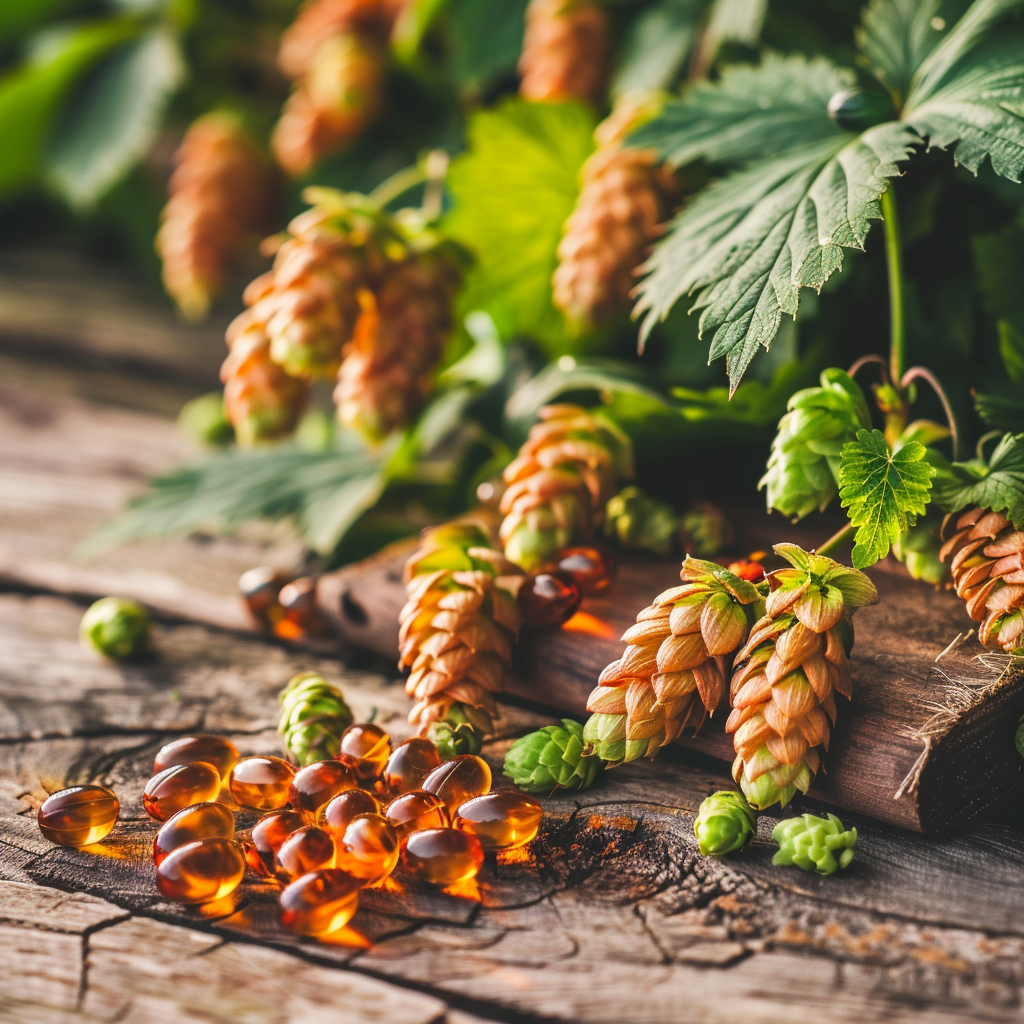

Iso-Alpha Acids
The primary ingredient in Iso-Alpha is a patented bio-available complex derived from the Hops plant. Each capsule contains Iso Alpha Acids and essential Polyphenol compounds scientifically proven to improve cognitive functions.

The Iso Alpha Acids in hops aren't limited to the brain - over 40 medical studies cover a number of medical issues including
✔ Memory Processing
✔ Attention Control
✔ Verbal Skills
✔ Mood Enhancement
✔ Mental Endurance
✔ Cognitive Flexibility
✔ Perceptual Learning
✔ Executive Function

Subscribe & Save
Try it risk free with our "walk on hot coals" guarantee. If you're not willing to walk on hot coals to keep your bottle, send it back for a full refund within 90 days.
Iso-Alpha Opens the Flood Gates to ...
-
Enhanced Cognitive Function
Focus, Learning, Mood & Memory
Activate the vagus nerve signaling the brain to release more acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and dopamine. -
Improved Memory and Focus
Mood, Creativity & Motivation
Boost your brain health by targeting the fdnc5 gene, which increases the production of the Irisin hormone, enhancing mental function and overall well-being. -
Enhanced Mood
Energy, Focus, Learning & Mood
Stimulate your gut-brain connection, naturally increasing norepinephrine, a key brain chemical linked to reducing symptoms of depression and ADHD.





Iso-Alpha
Iso-Alpha Brain Health
Share








Special Intro Pricing
This is your best chance to try iso-Alpha!
Questions You've Been Wondering
Will I feel the immediate effect of Iso-Alpha?
No, you will not feel an immediate effect. However, we guarantee within 60-90 days you will notice an improvement in your cognitive function, and mood.
What sets Iso Alpha apart from other products?
Most nootropics are botanicals that are destroyed in the stomach. Then, they travel in blood stream as proteins or nutrients, unlikely to actually benefit the brain as broken down components.
Iso-Alpha is made bioavailable, going into the stomach and reaching receptors immediately recognized by the body. From there, they cause a hormone release that affects the Vagus Nerve. This is a major nerve in the body. It signals to the brain release three important chemicals that may improve your cognitive function.
1. Acetylcholine
2. Norepinephrine
3. Dopamine
When you take Iso-Alpha Brain Health you will see that your brain starts to function a bit better each day. This is not an instant recovery but over time (60 days is recommended) you will likely see memory, focus and function improve.
How do I take Iso Alpha?
Take one capsule daily, preferably with a meal or water.
What does each bottle contain?
Each bottle holds a 30-day supply of brain fuel.
What are the contents of each pill?
Each Iso Alpha soft gel contains 100 mg of Hops Isohumulone and a patented bio-available polyphenol complex, alongside other ingredients such as polyglycerol esters of fatty acids, bovine gelatin, glycerin, purified water, and patented Hops Isohumulone.
Aren't there hops in beer?
Since iso-alpha acids (IAAs) are extracted from hops - the plant used to make beer - you're probably wondering if you can drink your way to enlightenment.
Well just so you know... In order to consume the 100mgs that are in a single capsule of iso-Alpha, you would have to down several six packs of the bitterest IPA beer.
Now, before you attempt that experiment - let me just tell you that we've already tried, and it definitely did NOT help us get more done at our desk. :-)
And before you try to order a big bulk sack of hops cones, you should know that eating hops doesn't work either.
That's why we've patented a new way to extract that IAAs hiding inside hop resin, and put them in a bioavailable capsule you take just once a day.
When should I expect to see benefits?
Unlike most nootropics that provide temporary effects, Iso Alpha offers lasting cognitive enhancements.
Significant improvements can typically be observed within 30 to 60 days.
What kind of benefits can I expect from taking Iso Alpha?
Iso Alpha, backed by over 40 scientific studies, enhances focus, mood, learning, motivation, creativity, memory, and more.
Is there a return policy if I'm unsatisfied?
You have a 60-day window to return the product for a refund, even if the bottle has been opened. We stand by our product's efficacy and offer a risk-free trial.


90 Day "Brain Boost" Guarantee
Use iso-Alpha every day for 90 days - and if you don't notice an impressive lift in your cognitive abilities - we'll gladly refund what you paid for our products!